L-Carnitine Description
L-Carnitine is a naturally occurring compound derived from amino acids that plays an essential role in energy metabolism. It functions primarily as a transporter molecule for long-chain fatty acids, shuttling them from the cytoplasm into mitochondria where they can be oxidized to produce energy.
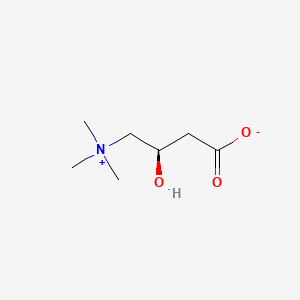
Chemically, L carnitine is known as 3-hydroxy-4-N-trimethylaminobutyrate. It exists in two stereoisomeric forms: L carnitine (the biologically active form) and D-carnitine.
In biochemistry, L-carnitine:
- Facilitates the transport of activated long-chain fatty acids across the inner mitochondrial membrane
- Helps regulate the ratio of acyl-CoA to free CoA in mitochondria
- Participates in removing toxic compounds from mitochondria
- Is involved in branched-chain amino acid metabolism
L-Carnitine Peptide Information
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C7H15NO3 |
| Molecular Weight | 161.2 g/mol |
| CAS Number | 541-15-1 |
| Synonyms | Levocarnitine, 541-15-1, (R)-Carnitine, Carnitor |
L-Carnitine Structure
Source: PubChem
Product Usage:
This PRODUCT IS INTENDED AS A RESEARCH CHEMICAL ONLY. This designation allows the use of research chemicals strictly for in vitro testing and laboratory experimentation only. All product information available on this website is for educational purposes only. This product should only be handled by licensed, qualified professionals. This product is not a drug, food, or cosmetic and may not be misbranded, misused or mislabeled as a drug.




Reviews
There are no reviews yet.